Using Keyboard Shortcuts rather than always relying on the mouse can save a load of time and therefore, increase productivity. Here are a few of the most useful Windows Keyboard Shortcuts available. I encourage you to try them out for yourself. You may soon be wondering how you got along without them.
Ctrl-A: Select all the items in the current window
Ctrl-C: Copy
Ctrl-V: Paste
Ctrl-X: Cut
Ctrl-Z: Undo
Ctrl-Esc: Start Menu (Useful on some laptops that don't have a Windows Key)
Ctrl-Shift-Esc: Open Task Manager
Ctrl-Tab: Change Child Window(i.e. Change to next tab in web browser)
F5: Refreshes the current window.
Tab: Move to next dialog box
Home: Moves display to top of the active window.
End: Moves display to bottom of the active window.
In the following group, 'Win' refers to the key with the Windows Logo on it.
Win-D: Show Desktop
Win-E: Windows Explorer
Win-F: Search or Find files
Win-R: Open Run dialog box
Win-Break: System Properties Dialog Box
Win-F1: Windows Help & Support Center
Alt-Enter (or Double-Click): Properties for selected object.
Alt-Tab: Switch between open applications
Alt-F4: Close Application/Window
Alt-Esc: Cycle through programs in the order that they were opened.
Shift-F10: Alt-Menu (or Right-Click)
Shift-Delete: Permanently Delete (By passes Recycle Bin)
Wednesday, October 7, 2009
Windows Keyboard Shortcuts
Monday, October 5, 2009
Windows Won't Boot!
If you are trying to boot to Windows NT, 2000, or XP and receive any of the following errors:
Windows could not start because the following file is missing or corrupt:
\WINDOWS\SYSTEM32\CONFIG\SYSTEM
Windows NT could not start because the below file is missing or corrupt:
X:\WINNT\System32\Ntoskrnl.exe
Windows NT could not start because the below file is missing or corrupt:
X:\WINNT\System32\HAL.dll
NTLDR is Missing
Press any key to restart
Invalid boot.ini
Press any key to restart
Your boot.ini file is missing, corrupted, or has errors in it. The boot.ini file contains a list of the operating systems installed on the hard drive and the boot options associated with those operating systems.
To repair the boot.ini file and get Windows booting again, you must use the Recovery Console. The Recovery Console allows users to perform tasks, using a command line interface(CLI), that will allow Windows to boot again. More on the Recovery Console here.
To use the Recovery Console from an install disk, make sure that your PC is configured to boot to your optical drive(that is a CD or DVD drive) and boot to the install disk.
After Windows Setup has finshed loading, you will be presented with a menu like the following:
This portion of the Setup program prepares Microsoft(R)
Windows(R) XP to run on your computer.
- To set up Windows XP now, press ENTER
- To repair a Windows XP installation using Recovery Console, press R
- To quit Setup without installing Windows XP, press F3
Of course, we want to press 'R' and use the Recovery Console.
Next you will be given a menu asking you to choose which Windows installation to log onto. Enter the number corosponding to the installation that needs to be repaired and press enter. Unless you have more than one operating system installed on your hard drive, you will only be presented with one option.
Now enter the Adminstrator password. If there isn't one, just press enter.
Now type 'cd ..' This will change directories to the root directory.
Next we need to delete the boot.ini file. To do so, the hidden, read only, and system file attributes must be removed. Enter the following commands:
C:\>attrib –h boot.ini
C:\>attrib –r boot.ini
C:\>attrib –s boot.ini
Now we can delete it
C:\>del boot.ini
Next we will use the bootcfg command. We will be using it to rebuild the bad boot.ini file that we just deleted. Read more about bootcfg here.
Enter the following command:
C:\>bootcfg /rebuild
After a few moments, you will see see a list of questions. The anwsers to these questions has been included:
Add installation to boot list? (Yes/No/All): Y
Enter Load Identifier: Microsoft Windows XP Professional Edition
Enter OS Load Options: /fastdetect /noexecute=optin
Obviously, the load identifier will change depending on which operating system you are working with. For further reading on the /fastdetect option. For more on /noexecute=optin
Your boot.ini file became corrupted somehow. Therefore, you should run the chkdsk utility to repair any errors on the harddrive. Please understand that this can take quite a while if you have a large hard drive or if you have a lot of errors. Enter the command:
C:\>chkdsk /r
Next enter the command:
C:\>fixboot
fixboot writes a new boot sector to the system partition.
That's all. We're done. You can now reboot by typing exit.
If Windows still won't boot, you will have to do a repair installation. More on that in an upcoming post.
Labels:
2000,
Boot Problems,
NT,
Recovery Console,
Windows,
XP
Friday, October 2, 2009
Missing 'Safely Remove Hardware' Icon
Here's a quick Windows' Tip. To properly remove a USB device, you should use the 'Safely Remove Hardware' icon which is located in the notification area of the task bar. The notification area is in the lower right corner, that is, the area where the clock is.
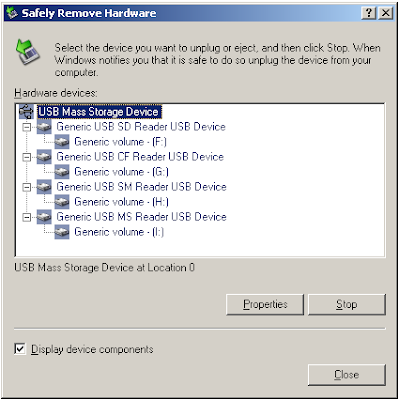
Simply unplugging a device without using 'Safely Remove Hardware' can cause damage to your files if, say, you are using an external USB storage device.
However, if the 'Safely Remove Hardware' icon is missing from the notification area, you can simply:
Press 'Start'(Also called the 'Windows Button')>Run>Then type 'RunDll32.exe shell32.dll,Control_RunDLL hotplug.dll'
Press 'Start'(Also called the 'Windows Button')>Run>Then type 'RunDll32.exe shell32.dll,Control_RunDLL hotplug.dll'

Now you can select the USB device that you wish to remove.
If you find that you need to do this often, you might want to create a desktop Shortcut. To do this, Right click an empty area on your desktop, Select 'New', then 'Shortcut', in the 'Type the location of the item:' dialog box enter 'RunDll32.exe shell32.dll,Control_RunDLL hotplug.dll'. Enter a name for your shortcut and you are finished.
Double-click your new shortcut any time you need to remove a USB device.
Thursday, October 1, 2009
Keyboard Skipping in Internet Explorer
For my first post I thought that I'd write about a problem that I had at work today. A customer was having a problem with his keyboard randomly skipping keys. The problem only occurred when he was using Internet Explorer. Therefore, we could easily conclude that the problem was not hardware related. Otherwise the keyboard would skip no matter the application in use. We could also conclude that the problem must be related to Internet Explorer.
Since the user had a lot of tool bars installed, I suspected the problem was related to an Add-on. Internet Explorer 7 introduced a feature that allows it to be started without any of the Add-ons loaded. To accomplish this:
Start>All Programs>Accessories>System Tools>Internet Explorer(No Add-ons)
This proved my suspicion. The keyboard worked perfectly.
Next, I needed to figure out which of the Add-ons was causing the problem. To do this:
Tools>Manage Add-ons...>Select an Add-on>Select 'Disable'
One way to find our problem Add-on would be to disable each Add-on one-by-one until the offending Add-on is revealed. This may indeed be the only way.
If you know that an Add-on has been recently installed in Internet Explorer or for some reason you have a 'bad feeling' about one of the Add-ons, this would, obviously, be the place to start. Otherwise, disable them one at a time until the problem is resolved.
Labels:
Add-ons,
Internet Explorer,
Keyboard,
Vista,
XP
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)




